Are you worried about whether Is bottom wisdom teeth gonna hurt more or top? You’re not alone! Many people feel anxious when it comes to wisdom tooth extraction, especially when it comes to figuring out which teeth might cause the most pain.
The truth is, the location of your wisdom teeth play a significant role in the level of discomfort you experience. In this article, we’ll dive into whether lower or upper wisdom teeth are more painful and why, helping you prepare for the procedure with confidence and ease.
Understanding why some teeth are more painful can help you prepare for the experience. This article explores whether the bottom wisdom teeth are indeed more painful than the top, the reasons behind this difference, and what you can do to alleviate the discomfort.
Differences Between Bottom and Top Wisdom Teeth Pain
Bottom wisdom teeth gonna hurt more and generally cause more pain than top ones due to differences in jaw structure and nerve sensitivity. The lower jawbone is denser and more resistant, making it harder for bottom wisdom teeth to break through the gums. This increased pressure can cause more discomfort and swelling. Additionally, the bottom jaw houses the inferior alveolar nerve, which is sensitive and can get irritated as the wisdom teeth emerge or become impacted, leading to sharp.
On the other hand, top wisdom teeth usually cause less pain because the upper jawbone is softer, allowing these teeth to emerge more easily. The top teeth are also located near the maxillary sinus, which has fewer nerves, resulting in less intense pain. When top wisdom teeth do become problematic, the pain is typically more localized and less severe.
In terms of extraction, removing bottom wisdom teeth is often more challenging due to the dense bone and proximity to critical nerves. This can lead to a longer and more uncomfortable recovery compared to the extraction of top teeth, which are generally easier to remove with less post-operative pain and swelling.
Causes of Wisdom Teeth Pain
Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the last set of teeth to emerge, typically between the ages of 17 to 25. While some people never experience problems with their wisdom teeth, many others face significant pain as these teeth try to come in. One of the primary causes of wisdom teeth pain is lack of space in the jaw. Most people’s jaws are not large enough to accommodate these additional teeth, which can lead to crowding. As the wisdom teeth push through the gums, they often exert pressure on the neighboring teeth, causing discomfort and pain.
Another common cause of pain is impaction. This happens when the wisdom teeth do not have enough room to emerge properly and become stuck, or impacted, beneath the gum line. Impacted teeth can grow at odd angles, sometimes even horizontally, pressing against other teeth and causing severe pain. This can also lead to swelling, infection, and even cyst formation if left untreated. Impacted wisdom teeth are one of the main reasons people need to have them surgically removed.
Additionally, wisdom teeth can cause pain due to inflammation and infection. When a tooth partially breaks through the gum, it creates an opening where food particles and bacteria can get trapped. This can result in an infection known as pericoronitis, which causes swollen, tender gums, bad breath, and a persistent ache in the jaw. If not treated, the infection can spread, leading to more serious health issues.
Since wisdom teeth are located at the very back of the mouth, they are harder to reach with a toothbrush or floss. This makes them more prone to cavities and gum infections. Poor oral hygiene around these hard-to-reach areas can lead to decay, which causes pain similar to that of a regular toothache but is often harder to treat due to the tooth’s position.
Signs That Your bottom wisdom teeth gonna hurt
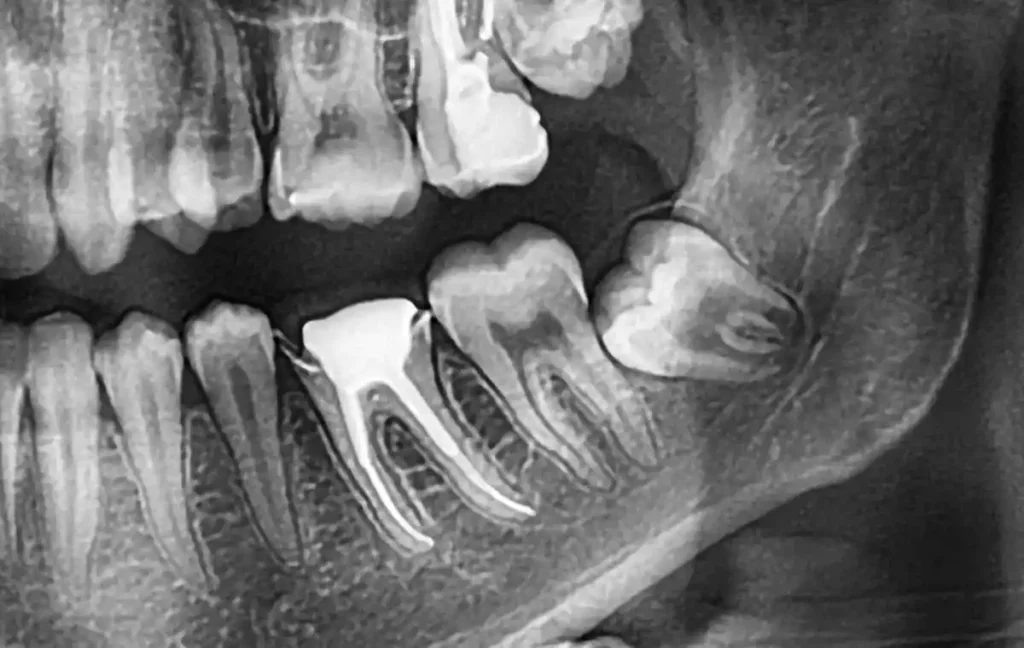
Persistent Throbbing or Aching Pain in the Lower Jaw
One of the most common signs that your bottom wisdom teeth are causing problems is a persistent throbbing or aching pain in the lower jaw. This pain often starts as a dull discomfort but can gradually intensify as the teeth continue to push against neighboring teeth or the dense lower jawbone. The pain may become more noticeable when you chew, speak, or open your mouth wide.
Swelling and Tenderness Around the Gums
If you notice swelling, redness, or tenderness at the back of your mouth near your lower molars, it’s a clear sign that your bottom wisdom teeth might be struggling to emerge. The inflammation can be caused by the teeth trying to break through the gum tissue, often leading to discomfort and puffiness in the surrounding area. This swelling can also make it painful to brush or floss the back of your mouth.
Difficulty Opening Your Mouth or Chewing
Another sign is experiencing difficulty opening your mouth fully or feeling pain while chewing. As the bottom wisdom teeth press against the jawbone or other teeth, it can cause tightness and soreness in the jaw muscles. This restriction can make it hard to open your mouth completely, leading to pain when eating or speaking.
Bad Breath and Unpleasant Taste in Your Mouth
If you’re noticing persistent bad breath or a foul taste, it could be due to an infection around a partially erupted wisdom tooth. When bottom wisdom teeth don’t fully break through the gum line, they create pockets where food particles and bacteria can accumulate. This can result in an unpleasant taste, bad breath, and even an infection known as pericoronitis if not treated promptly.
How Dentists Determine Whether Bottom or Top Wisdom Teeth Need Removal
- X-rays: Dentists take X-rays to see the position of the wisdom teeth and check if they are impacted or growing at an angle.
- Signs of Crowding or Pain: If wisdom teeth are causing pain, crowding other teeth, or pushing them out of alignment, removal may be necessary.
- Risk of Infection: Partially erupted teeth are more prone to infections. Dentists assess if the wisdom teeth are difficult to clean and likely to cause gum infections.
- Nerve Proximity: For bottom teeth, dentists check how close they are to the inferior alveolar nerve. If there’s a risk of nerve damage, removal may be more carefully planned.
- Jaw Space and Alignment: Dentists evaluate if there’s enough room in the jaw for the teeth to fully emerge without causing issues. Lack of space often means extraction is the best option.
Tips to Manage Pain from Bottom Wisdom Teeth
Take Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
One of the most effective ways to alleviate pain from bottom wisdom teeth is to use over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. These medications help reduce inflammation, which is often the source of pain, while also providing relief from the throbbing sensation that can occur in the jaw. Be sure to follow the recommended dosage on the packaging to avoid any side effects. Pain relievers can be especially helpful if the pain is making it difficult to eat or sleep.
Use Cold Compresses to Reduce Swelling
Applying a cold compress to the outside of your jaw can be a quick way to numb the area and ease discomfort. The cold temperature helps constrict blood vessels, reducing swelling and numbing the pain. Wrap some ice or a cold pack in a towel and hold it against your cheek for about 15-20 minutes at a time. This can be repeated several times a day, especially during flare-ups, to manage pain and swelling effectively.
Rinse with Warm Salt Water for Gum Relief
A simple saltwater rinse can work wonders for pain relief, especially if your wisdom teeth are partially erupted. This helps cleanse the area, reduces bacteria, and soothes swollen or irritated gums. Doing this a few times a day can help prevent infections and provide natural pain relief.
Pain Levels Between Top and Bottom Wisdom Teeth
| Factors | Top Wisdom Teeth | Bottom Wisdom Teeth |
| Bone Density | Less dense, easier to extract | Denser bone, more painful extraction |
| Nerve Sensitivity | Fewer nerve complications | Higher risk of nerve irritation |
| Risk of Impaction | Lower risk | Higher risk |
| Typical Pain Levels | Generally less painful | Often more painful |
| Recovery Time | Shorter | Longer due to surgical complexity |
Conclusion:
So, is bottom wisdom teeth gonna hurt more or top? In most cases, the answer is yes. The denser bone structure of the lower jaw, coupled with its complex nerve network, means that pain and discomfort are often more pronounced for bottom wisdom teeth.
Whether you’re dealing with existing pain or considering extraction, being informed can make the process less daunting. Understanding the differences between top and bottom wisdom teeth and knowing how to manage the pain effectively will help you make better decisions for your dental health.
By staying proactive, consulting with your dentist, and using effective pain management techniques, you can ease the discomfort associated with wisdom teeth, ensuring a smoother and quicker recovery.


1 thought on “Is bottom wisdom teeth gonna hurt more or top”